User environment
User workspace
The default login shell for your user account is bash. To determine your current login shell :
$ echo $SHELL
By default, the login shell change directory to $HOME folder.
Each user has 2 folders ($HOME and $WORK) organized as follows:
| Directory | Environment variable | File system | Backup | Quota |
|---|---|---|---|---|
/users/<login> | $HOME | NFS | Protected | 20 Gio |
/work/mesobfc/<login> | $WORK | BeeGFS | No | 8 Tio |
$WORKis used as working directory: all simulation data must be copied in this folder.$HOMEis read-only in computing nodes (batch).
To display your quota usage for $HOME and $WORK, you can use the command show-disk-quota.
Using modules to manage your environment
Installed applications are organized using module command according to the architecture of the node (Intel, AMD).
The module command supports the following subcommands:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
module display <module> | Display what a module does |
module list | List loaded modules |
module avail | List all the modules which are available to be loaded |
module load <mod1> [mod2...] | Load a module |
module unload <module> | Unload a module |
module purge | Unload all modules (purge) |
For example on the login node, one can view all installed/available package software:
$ module avail -t
/soft/spack/share/spack/modules/linux-rocky8-x86_64:
miniconda3-22.11.1/gcc-13.1.0
/soft/spack/share/spack/modules/linux-rocky8-skylake_avx512:
cp2k-2023.2/openmpi-4.1.5/gcc-13.1.0-openblas
gromacs-2023.1/double/openmpi-4.1.5/gcc-13.1.0-openblas
octopus-12.2/gcc-13.1.0-openblas
openmpi-4.1.5/gcc-13.1.0
openmx-3.9/gcc-13.1.0-openblas
quantum-espresso-7.1/gcc-13.1.0-openblas
wps-4.3.1/gcc-13.1.0-ccub_no_leap
wps-4.3.1/gcc-13.1.0-ccub_no_leap-serial_NO_GRIB2
wps-4.3.1/gcc-13.1.0-serial_NO_GRIB2
wrf-4.3.3/gcc-13.1.0-ccub_fcoptim
wrf-4.3.3/gcc-13.1.0-ccub_fcoptim-ccub_no_leap
/soft/spack/share/spack/modules/linux-rocky8-icelake:
cp2k-2023.2/openmpi-4.1.5/gcc-13.1.0-openblas
gromacs-2023.1/double/openmpi-4.1.5/gcc-13.1.0-openblas
hpl-2.3/gcc-13.1.0-openblas
namd-2.14/gcc-13.1.0
octopus-12.2/gcc-13.1.0-openblas
openmpi-4.1.5/gcc-13.1.0
openmx-3.9/gcc-13.1.0-openblas
osu-micro-benchmarks-7.1-1/gcc-13.1.0
siesta-4.0.2/gcc-13.1.0-openblas
wps-4.3.1/gcc-13.1.0-ccub_no_leap
wps-4.3.1/gcc-13.1.0-ccub_no_leap-serial_NO_GRIB2
wrf-4.3.3/gcc-13.1.0-ccub_fcoptim-ccub_no_leap
- The management of modules according to the node architecture is provided by Spack software.
- Module name is generated according to the software version, compiler version and even MPI version if enabled.
For example to load and use openmx-3.9/openmpi-4.1.5/gcc-13.1.0-openblas (OpenMX version 3.9 compiled with GCC-13.1.0
and OpenMPI 4.1.5 and openblas lib)
$ module load openmx-3.9/openmpi-4.1.5/gcc-13.1.0-openblas
Transfer data from/to MesoBFC
Using SSH command line
These commands must be executed on your local machine !
- To copy files from your
localhosttoMesoBFC:
$ scp file1 file2 login@login-1.mesobfc.fr:WORK
This command will copy file1 and file2 to directory WORK on MesoBFC.
- To copy files from
MesoBFCto yourlocalhost:
$ scp login@login-1.mesobfc.fr:WORK/files.tgz .
This command will copy files.tgz from directory WORK on MesoBFC to your current directory on localhost.
Using graphical tools
FileZilla is a good Graphical User Interface (GUI) to SFTP protocol (based on SSH).
Use the same credentials as with ssh/scp and use port 22 to use SFTP protocol.
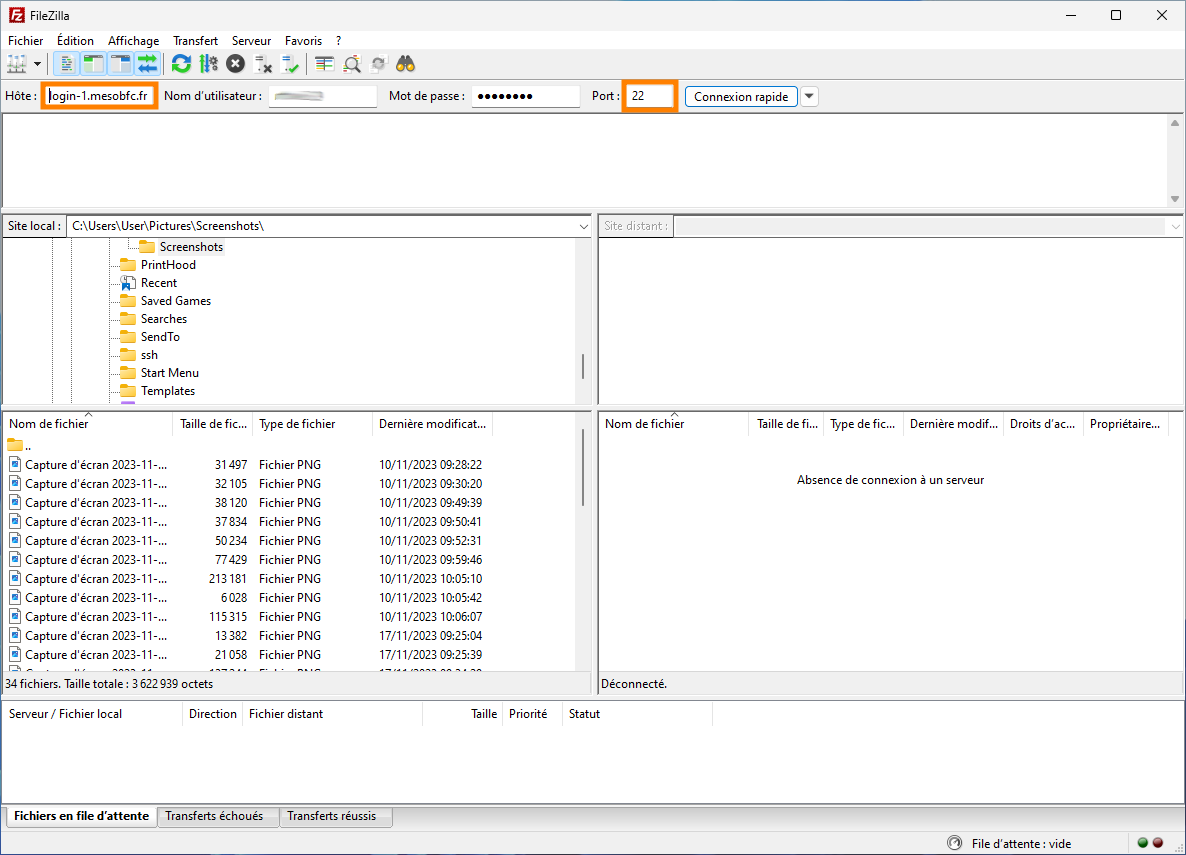
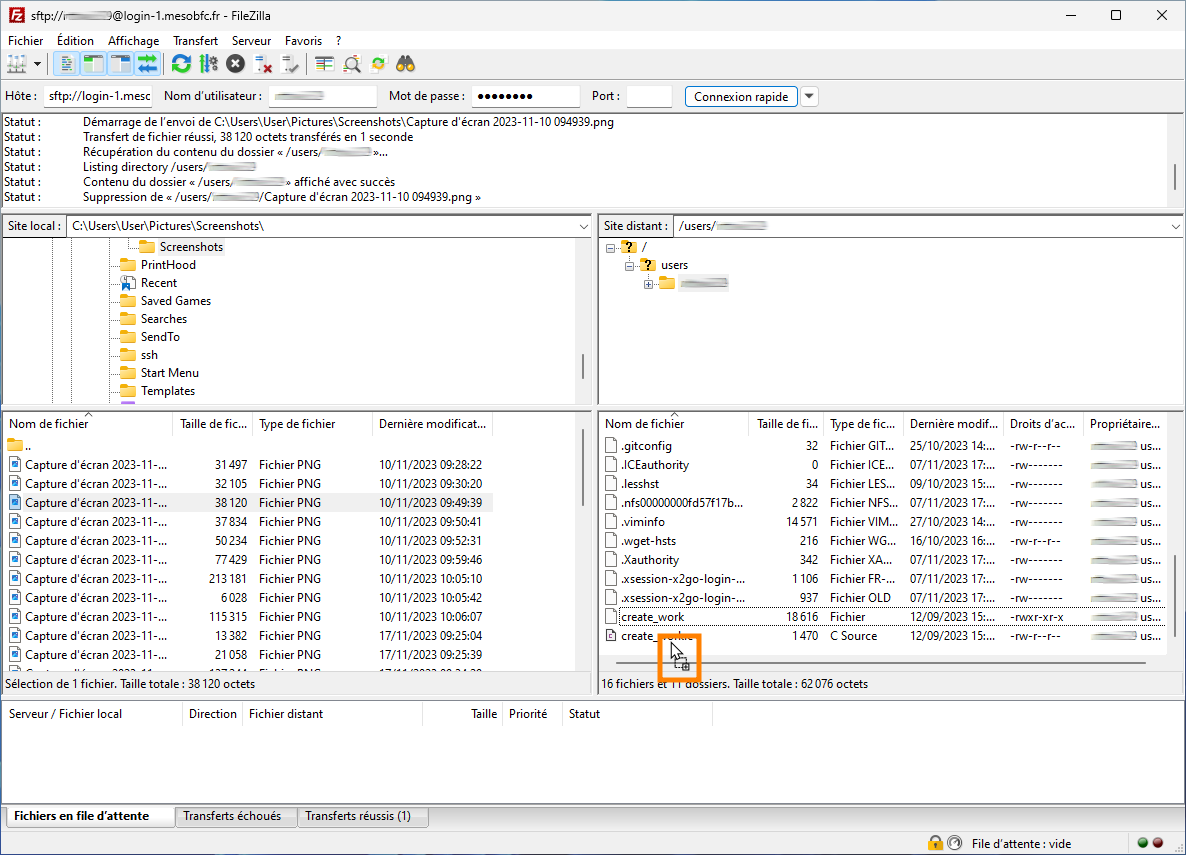
Once connected, you can simply transfer files by drag & drop operations or by right-clicking in the file(s) you wish to transfer.
Citizenship on MesoBFC
Be always aware that you are working on a shared system where your behavior could have a negative impact on the workflow of other users.